The Intel Core i5 was once overlooked by a lot of gamers, computer builders, and enthusiasts. It wasn’t necessarily horrible, but for many years it was a touch boring. We have been (im)patiently awaiting the Core i5-12600 replacement K’s since that changed with the Core i5-12600K. And that replacement, the Intel Core i5-13600K, is now available.
Even though it is unlocked, it is still a mid-tier CPU in Intel’s portfolio. Additionally, it continues to use the same Intel 7 processor as the 12th Gen. It couldn’t really be that good, could it?

The Core i5 from the 12th generation offers a major upgrade over its predecessors, much like every other model in Intel’s lineup. The Intel Core i5 13600K is therefore only more, even though it still uses the same manufacturing process and has the same hybrid design with performance cores (P-cores) and efficiency cores (E-cores). All 13th-generation chips have twice as many E-cores as those from the previous generation. All of them offer enhanced performance at both maximum load and reduced power demands. And like the Core i9-13900K, the Core i5-13600K delivers in spades.
This is the finest CPU to purchase if you’re a PC gamer and are currently building a new computer without a doubt.
Intel Core i5 13600K Specifications

The 13th Gen Core “Raptor Lake” family, including the Intel Core i5 13600K, features generational advancements in CPU core count. The chip has six P-cores (performance cores) and eight E-cores (E-cores).
While it may seem insignificant given that only the E-core count has increased, Intel also replaced the P-cores with the new “Raptor Cove” ones that come with higher IPC, larger caches, and faster clock speeds. This 6P+8E arrangement is superior than the 6P+4E configuration of the i5-12600K “Alder Lake” generation.
A swarm of physically smaller E-cores handles most light to moderate workloads, and in a crunch situation (all cores loaded); b the silicon only has six or eight P-cores, which Intel wagers are sufficient for taking on compute-intensive less parallelized tasks; and c the 13th Gen Core “Raptor Lake” helps Intel shore up CPU core-counts and chase down AMD’s lead in that area.
Intel is smart about it. As a result, AMD’s advantage in terms of gaming performance can be overcome by P-cores with high clock rates, while its advantage in terms of multi-threaded creation workloads can be eliminated by E-cores operating in tandem with P-cores.
Intel is introducing new “Raptor Cove” P-cores with “Raptor Lake” that have higher IPC (single-threaded performance at a given clock speed), the ability to sustain higher clock speeds generationally, and higher amounts of dedicated L2 cache—increased to 2 MB compared to 1.25 MB on the “Golden Cove” cores of “Alder Lake.” The E-core counts, clock rates, and L2 cache sizes have all increased generationally even while the “Gracemont” E-cores remain the same.
As opposed to “Alder Lake,” each “Gracemont” 4-core cluster now shares 4 MB of L2 caches among the cores. Eight E-cores and two of these clusters are present in the Core i5-13600K. Additionally, the shared L3 cache size has grown to 24 MB from 20 MB on the i5-12600K.

Even though they are accompanied by motherboards from the 700-series chipset family with enhanced power architecture and downstream PCIe connectivity, the 13th Gen Core “Raptor Lake” processors are compatible with existing Intel 600-series chipset motherboards via BIOS updates.
They are built on the same Socket LGA1700 package as the 12th Gen. With one PCI-Express 4.0 x4 NVMe slot connected to the CPU, DMI 4.0 x8 chipset-bus, and PCI-Express 5.0 x16 PEG, the new processors support the same I/O as the 12th Gen. The processors support DDR4 and DDR5 memory formats, giving customers more options.
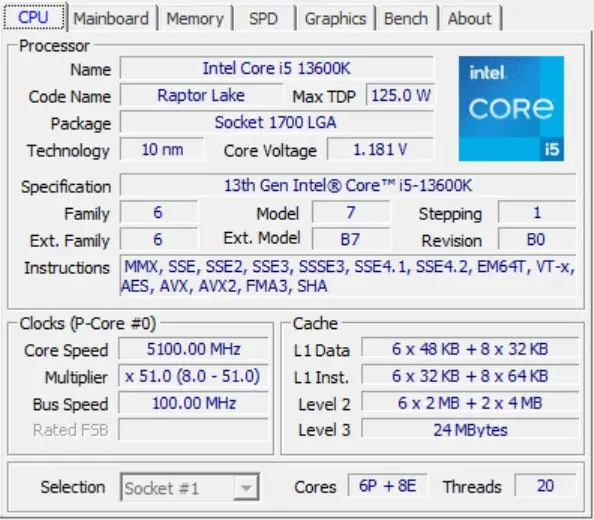
Intel Core i5 13600K Essential Information
| Product Collection | 13th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Processors |
| Code Name | Products formerly Raptor Lake |
| Vertical Segment | Desktop |
| Processor Number | i5-13600K |
| Status | Launched |
| Launch Date | Q4’22 |
| Lithography | Intel 7 |
| Recommended Customer Price | $319.00 – $329.00 |
| Use Conditions | PC/Client/Tablet |
Intel Core i5 13600K Specs
| Total Cores | 14 |
| # of Performance-cores | 6 |
| # of Efficient-cores | 8 |
| Total Threads | 20 |
| Max Turbo Frequency | 5.10 GHz |
| Performance-core Max Turbo Frequency | 5.10 GHz |
| Efficient-core Max Turbo Frequency | 3.90 GHz |
| Performance-core Base Frequency | 3.50 GHz |
| Efficient-core Base Frequency | 2.60 GHz |
| Cache | 24 MB Intel® Smart Cache |
| Total L2 Cache | 20 MB |
| Processor Base Power | 125 W |
| Maximum Turbo Power | 181 W |
Intel Core i5 13600K Benchmarks & Tests
The Intel Core i5 13600K is used in the tests, which are run on a Maximus ROG Z790 Hero motherboard with 32GB (2x16GB) of G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo EXPO CL30 RAM operating at DDR5-5600 standard specifications (CL30). The supporting cast includes an Nvidia GeForce RTX 3080 FE graphics card, a Seagate FireCuda 530 2TB SSD, and Noctua NH-D15 cooling, which are likewise shared by all processors. Be quiet! batteries power the group. PSU Dark Power 13, 1000W. The evaluation chip is operated at a maximum power setting of 181W, as required by Intel.
The Core i5-13600K easily surpasses the Core i7-12700K in the majority of CPU tests. With a total of 12 cores, the Core i7-12700K debuted on the market last year for $409 and has almost as many (eight P-cores, four E-cores). With two fewer P-cores, twice as many E-cores, and 8MB more L2 cache, the Core i5-13600K is $80 less expensive.

With this knowledge, it was plausible that these CPUs would alternate positions based on the test, however, the Intel Core i5 13600K outperforms them all. In certain tests, it doesn’t win by a large margin, but it does succeed. In contrast, the Core i5-12600K was left in the dust, and in several tests, the Core i5-13600K even managed to outperform the 16-core Ryzen 9 7950X. (However, as you might anticipate, the Core i5 fell far short of the 16-core/32-thread Ryzen 9 7950X in the majority of tests.)
The Intel Core i5 13600K is more evenly matched by AMD’s Ryzen 7 7700X, although Intel still holds some significant advantages. In seven of the eight tests, the Core i5-13600K triumphs over the Ryzen 7 7700X, but sometimes by very small margins. The only test in which the Ryzen 7 7700X narrowly prevails over the Core i5-13600K is Adobe Photoshop. It becomes challenging to defend the Ryzen 7 7700X when you consider that it costs $170 more than the Core i5-13600K.

With the exception of the Core i5-13600K and the AMD Ryzen 7 5700X, it is difficult to make a compelling case for any of the processors in the aforementioned list when it comes to gaming. The Core i5 competes favorably with the finest of them while costing less than the majority of its rivals.
Although the Ryzen 7 5700X starts at $299 and its immediate predecessor is available for $40 cheaper, both similarly suffer from a significant performance hit. In contrast, the AMD Ryzen 7 5700X performs somewhat worse in most games but is also more affordable, making it a good choice for those on a tighter budget if the AMD AM4 architecture (and possibly reusing some DDR4 RAM) is the best choice for them.
Intel Core i5 13600K Conclusion
Let’s get to the point without delay. The $319 Intel Core i5 13600K is an excellent CPU that defies its mid-range label to deliver outstanding performance in both apps and games.
By improving upon the previous generation and gaining weight in all the right places, Intel excels in the areas that matter the most. The cherry on top is that Intel softens the blow to adoption by enabling compatibility with affordable B660 motherboards and widespread DDR4 memory. Rival AMD’s emerging Ryzen 7 7700X and Ryzen 5 7600X are challenged in nearly every situation.

The mid-range champion, which aims for perfection in everything it does, supersedes most 12th-gen chips. Anyone who has invested in a Core i9-12900KS will be left wondering how an i5 is able to outperform their precious CPU in gaming while grinning ruefully.
Intel’s Core i5-13600K is a true jewel, behaving like the finest Cores of 2021 and giving price-comparable Ryzens a bloody nose. The person to choose.
Is the Intel Core i5 13600K worth it?
With 14 cores and 20 threads, the Intel Core i5 13600K is a powerful processor for multitasking and gaming. Its base clock is 3.5 GHz, and its boost clock is 5.1 GHz. It is compatible with both DDR4 and DDR5 memory. If your motherboard and cooling system are suitable, it can also be unlocked for overclocking.
Reviews claim that the AMD Ryzen 5 7600X is either surpassed or tied by the Intel Core i5 13600K, making it one of the best processors in its price category. Additionally, it is a major upgrade over the Core i5 12600K of the previous generation, which had fewer cores and slower clock speeds.
The Intel Core i5 13600K does, however, have many disadvantages, including increased heat production, higher power consumption, and a higher price than its predecessor. If you want to upgrade from an older Intel CPU, you will also need a new motherboard because it requires a new LGA 1700 socket.
Ultimately, your budget, your existing system, and your performance requirements will determine whether the Intel Core i5 13600K is worth it. The Intel Core i5 13600K is a fantastic option if you’re searching for a powerful CPU that can easily handle the majority of games and programs and you don’t mind updating your motherboard and paying a little bit extra. However, you might want to wait for a price reduction or a better bargain if you have a limited budget or currently own a good processor that satisfies your needs.
Is Intel Core i5 13600K good for gaming?
An excellent processor for gaming is the Intel Core i5 13600K, which provides good performance in most games at resolutions of 1080p and 1440p. Reviews claim that in the majority of benchmarks, the AMD Ryzen 5 7600X, another well-liked gaming CPU, is beaten or tied by the Intel Core i5 13600K. In addition, compared to the Core i5 12600K of the previous generation, it features more cores, a faster clock, and a bigger cache.
The Intel Core i5 13600K does, however, have many disadvantages, including increased heat production, higher power consumption, and a higher price than its predecessor. If you want to upgrade from an older Intel CPU, you will also need a new motherboard because it requires a new LGA 1700 socket.
The Intel Core i5 13600K’s suitability for gaming ultimately comes down to your needs in terms of performance, budget, and existing system. The Intel Core i5 13600K is a fantastic option if you’re searching for a powerful CPU that can easily handle the majority of games and programs and you don’t mind updating your motherboard and paying a little bit extra. However, you might want to wait for a price reduction or a better bargain if you have a limited budget or currently own a good processor that satisfies your needs.
The Intel Core i5 13600K is anticipated to be a fantastic option if your main purpose for designing a system is gaming, especially with its balance of performance and pricing. For the best gaming experience, it must be combined with a strong graphics card though, as the GPU is frequently an important component of gaming setups.
Can you overclock the Intel Core i5 13600K?
Since the Intel Core i5 13600K is an unlocked processor with manual frequency and voltage adjustments supported, the answer is yes—you can overclock it. But in order to overclock, you’ll need a good cooling system, a suitable motherboard, and some technical know-how. In addition, overclocking can raise your system’s noise, heat production, and power consumption. If done improperly, it can also void your warranty or break your hardware.
You might be able to attain a steady overclock of 5.5 GHz or more on all P-Cores, which can greatly improve the performance of your games and applications, depending on your cooling system and CPU quality. Overclocking is not always possible and can vary from system to system, therefore you should always exercise caution and keep a close eye on your system.
It’s crucial to remember that overclocking can violate your CPU’s warranty and that managing the increased heat generation calls for an effective cooling solution. When overclocking, always exercise caution and knowledge, and be mindful of the limitations of the CPU and cooling system you are using.
It’s a good idea to check for the most recent information in the motherboard user manual and any applicable BIOS/UEFI upgrades, as information can change and new features or guidelines may have been released since my last update. Community forums and motherboard- and processor-specific overclocking guides can often offer helpful advice and insights.
What temperature should an Intel Core i5 13600K run at?
A strong processor that can operate at high temperatures under intense load is the Intel Core i5 13600K. The published specs state that the CPU’s maximum temperature (TJUNCTION) is 100°C. It is not necessary for the CPU to operate at this temperature all the time, though, as it could shorten its life and performance.
The cooling system, outside temperature, overclocking settings, workload, and other variables all affect the ideal temperature range for the Intel Core i5 13600K. Lower temperatures often help the CPU because they can avoid thermal throttling and increase stability. Less heat, noise, and money may also be needed for the cooling system at lower temperatures.
Reviews claim that the Intel Core i5 13600K can operate at 60–70°C on average and 80–85°C at its highest while playing demanding games and utilizing a good liquid cooling system. As long as the temperatures stay below the TJUNCTION limit, these are regarded as normal and safe for the CPU. But, if you wish to overclock the CPU, you might require additional voltage and a better cooling system, which can raise the temperature noticeably.
The optimal operating temperature of the Intel Core i5 13600K ultimately comes down to trade-offs and personal preference. Lower temperatures are ideal for maximizing CPU performance and lifespan, but you’ll have to put up with more noise and spend more money on the cooling system. You can withstand greater temperatures if you don’t mind moderate performance and lifespan, but take care not to damage the CPU or surpass the TJUNCTION limit.
How much power does the Intel Core i5 13600K draw?
With 14 cores and 20 threads, the Intel Core i5 13600K has a processor base power (PBP) of 125 W. Nevertheless, this figure does not accurately represent the CPU’s real power usage over a range of workloads and overclocking configurations. The greatest power that the CPU can draw when increasing its frequency is known as the maximum turbo power, and it is 181 W. This is more than the 150 W maximum turbo power of the Core i5 12600K from the previous generation.
Intel Core i5 13600K
-
Performance - 98%98%
-
Price - 97%97%
-
Value - 98%98%

